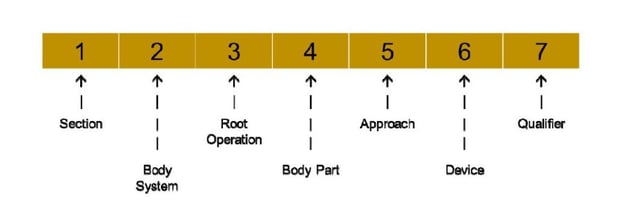
Before we jump into part four, please note the seven characters for medical and surgical procedures section and their meanings:
10. Biopsy Diagnostic Qualifier X
The problem in this instance is that coders are not applying the 7th character “X-Diagnostic” correctly.
Biopsy Diagnostic Qualifier X: B3.4a
Biopsy procedures are coded using the root operations Excision, Extraction, or Drainage and the qualifier Diagnostic. The qualifier Diagnostic is used only for biopsies.
A colonoscopy with biopsy of transverse colon is coded to root operation Excision and qualifier Diagnostic. If a colonoscopy is done to remove a polyp, and the polyp is sent to pathology, do NOT use qualifier X –diagnostic.
Biopsy with Definitive Treatment: B3.4b
If a diagnostic Excision, Extraction, or Drainage procedure (biopsy) is followed by a more definitive procedure, such as Destruction, Excision or Resection at the same procedure site, both the biopsy and the more definitive treatment are coded.
Biopsy of lesion of the left parotid gland, followed by resection of entire left parotid gland – codes are assigned for both the diagnostic Excision and Resection of left parotid gland.
Example: Excision of RUL of Lung Due to Cancer
Patient has undergone previous CT of the lung with identification of a right upper lobe mass, and patient was scheduled for surgery to remove the mass. Patient is admitted inpatient and undergoes open removal of the mass right upper lobe with margins. The specimen is sent to pathology where adenocarcinoma of the lung is diagnosed. The lung tissue margins are clear. The patient is discharged.
Would the coder assign the 7th character of “X Diagnostic” to the excision code?
No, for the case where a planned mass excision from the right upper lobe is performed, only one code for the excision of the mass is assigned with qualifier Z.
Example: Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Wedge Resection
History & Physical Examination (H&P): “Mr. XXX is here today to discuss options for diagnosing his progressive diffusing capacity dysfunction, now down to 59% predicted. He has significant exposure history including smoking. Previous FOB/BAL showed eosinophilia and was thought to be related to medications that has since been stopped. He is here to discuss tissue diagnosis… Mr. XXX has what appears to be progressive and diffuse pulmonary interstitial disease. There is volume loss in the right hemi thorax. No significant mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Would agree with tissue sampling to make a definitive diagnosis of the cause of the fibrosis…”
Op note: “…Right-sided video-assisted thoracoscopic exploration with wedge resection of the middle lobe and the upper lobe…”
Indication for the procedure: “…an unfortunate 68-year-old gentlemen who presents with worsening SOB and dyspnea on exertion. He has undergone bronchoscopy in the past with biopsies, brushing and cultures and these have been diagnostic. His disease has progressed and he was therefore, referred for possible tissue biopsy.”
Op note: “… I palpated the lung, and along with the tactile stimulus, as well as CT scan findings, the areas were chosen in the upper lobe, as well as the middle lobe for biopsy. An Endo-GIA stapler was used to divide these small portions of lung from the remainder of the lung. These both were placed in an EndoCatch pouch. A small portion of each specimen was sent for microbiology and gram stain, culture and sensitivity. The remaining majority of the specimen was sent for permanent analysis.”
Pathology: Lung, right middle lobe, wedge biopsy shows advanced interstitial pneumonia with a usual interstitial pneumonia pattern.
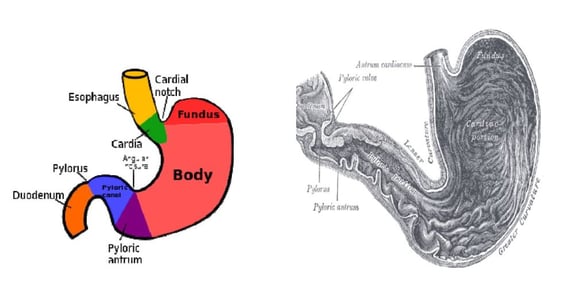
11. EGD with Biopsy Body Parts
The problem is that many times during EGD, the physician biopsies the antrum of the stomach. ICD-10-PCS assigns this body part to stomach, pylorus.
Antrum of Stomach classified as Pylorus
The index says for pyloric antrum, use stomach, pylorus. This includes pyloric antrum; pyloric canal and; pyloric sphincter.
Dorland’s Medical Dictionary states: “antrum, pyloric is the dilated portion of the pyloric part of the stomach, distal to the body of the stomach and proximal to the pyloric canal. It is also called also gastric antrum and antrum of stomach… “pylorus, the distal aperture of the stomach, opening into the duodenum, variously used to mean pyloric part of the stomach and pyloric antrum, canal, opening or sphincter.”
EGD with Biopsy of Antrum: 0DB78ZX
The information contained in this coding advice is valid at the time of posting. Readers are encouraged to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with the topic as they can change rapidly.