4. Glasgow Coma Scale
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) codes should now be reported when documented on any case where there is monitoring of the central nervous system regardless of the medical condition requiring the monitoring.
At a minimum, report the initial score documented on presentation to your facility.
The documentation of the coma scale may be by other clinicians involved in the care of the patient (EMT, nursing) and not only by the physician.
5. Periprosthetic Fractures
This was a problem even before ICD-10 in determining S code vs T84.04 and sequencing.
The specific traumatic or pathological fracture code by site is coded and assigned first, followed by a code in category M87. Category M97 is assigned for a true periprosthetic fracture. Category code T84. is reserved for true prosthesis malfunction or problems.
The good news: Code T84.04 has been deleted.
An example of coding a traumatic periprosthetic fracture of the lower end of the right femur is:
-
- S72.401A, Unsp fracture of lower end of right femur, initial encounter for closed fracture
- M97.01XAA, Periprosthetic fracture around internal prosthesis of right hip joint, initial encounter
- Appropriate external cause codes
6. Rehabilitation Unit Principal Diagnosis
Assigning the reason for admission to rehab as PDX was introduced in ICD-10; there is no equivalent to old ICD-9-CM V57 codes.
Here’s a scenario:
86 year old with mobility and selfcare dysfunction after hospitalization for CHF exacerbation. The patient has a history of multiple spinal fusion and laminectomy procedures. The patient continues to require inpatient rehabilitation for functional upgrade return to community living. He requires PT and OT for at least 3 hours daily 5 days a week to address his debility, focusing on improving mobility ambulation and ADLs. Patient’s functional goals are to get his strength back after his last few months of surgeries and illnesses and return home.
So what is the PDX for the UB04? Debility? CHF?
- There seems to be conflicts with Coding Clinic 4Q 2013 page 129 and Coding Clinic 4Q 2012 pages 90-99:
- CC 4Q 2013: patient transferred to rehab unit for OT and PT following prolonged stay at a LTCH where patient was weaned from mechanical vent. Patient received rehab due to deconditioning and debility. The provider documented that the patient presented with complex medical problems that included chronic hypoxic respiratory failure, COPD, diabetic neuropathy and obesity.
- Assign J96.11, Chronic respiratory failure with hypoxia as PDX. This is the underlying reason for and deconditioning and the underlying reason is coded as the principal diagnosis.
- Coding Clinic 4Q 2012 pages 90-98 states that when a patient is admitted to LTC nursing home for “deconditioning” coders should code the symptoms of deconditioning such as gait disturbance, weakness, etc.
- CC 4Q 2013: patient transferred to rehab unit for OT and PT following prolonged stay at a LTCH where patient was weaned from mechanical vent. Patient received rehab due to deconditioning and debility. The provider documented that the patient presented with complex medical problems that included chronic hypoxic respiratory failure, COPD, diabetic neuropathy and obesity.
So which is correct?
The rehabilitation principal diagnosis would be congestive heart failure. Refer to the following Coding Clinics for additional guidance.
- When an injury is reason for rehabilitation
- Coding Clinic 4Q 2013 pages 90-98 and 128-129
- If a patient is transferred to LTC (or rehab) following hospital stay for treatment of fracture or injury such as pelvic and clavicular fracture, assign the S32.9XXD with 7th character of D, subsequent encounter.
- Review Coding Clinic 3Q 2015 page 36
- Discusses IRF-PAI vs UB04 coding
- Review Coding Clinic 1Q 2015 page 21
- Rehabilitation services are not considered active treatment and the encounter should be reported with the appropriate 7th character for “subsequent encounter.”
Another common question is on OCG II PDX K. admissions/encounters for rehabilitation. When the purpose for the admission/encounter is rehabilitation, sequence first the code for the condition for which the service is being performed. For example, for an admission/encounter for rehabilitation for right-sided dominant hemiplegia following a cerebrovascular infarction, report code I69.351, Hemiplegia and hemiparesis following cerebral infarction affecting right dominant side, as the first-listed or principal diagnosis.
If the condition for which the rehabilitation service is no longer present, report the appropriate aftercare code as the first-listed or principal diagnosis. For example, if a patient with severe degenerative osteoarthritis of the hip, underwent hip replacement and the current encounter/admission is for rehabilitation, report code Z47.1, Aftercare following joint replacement surgery, as the first-listed or principal diagnosis. (See Section I.C.21.c.7, Factors influencing health states and contact with health services, Aftercare.)
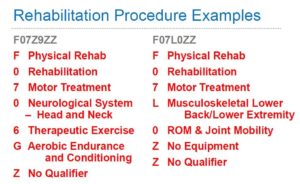
In some cases adding the rehabilitation ICD-10-PCS code when paired with a diagnosis code that is included within MDC 23 will change your DRG to 945/946. Many diagnosis codes assigned for rehab patients do not end up in MDC 23.
Here’s a scenario:
Patient admitted to rehab with S02.119D, Unspecified fracture of occiput, subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing, is included in MDC 8. Adding a procedure code such as F0706GZ (Therapeutic Exercise Treatment of Neurological System – Head and Neck using aerobic endurance and conditioning equipment) would NOT lead to DRG 945/946.
However, assigning Z51.89, Encounter for other specified aftercare or Z44.9, Encounter for fitting and adjustment of other external prosthetic devices with this procedure will lead to DRG 945/946.
The information contained in this coding advice is valid at the time of posting. Readers are encouraged to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with the topic as they can change rapidly.